.jpg)
This is often heavily negotiated because, in industries like manufacturing, the provenance of their assets comprise a major part of their company’s top-line worth. This means that the computer will be used by Company A for 4 years and then sold afterward. The company also estimates that they would be able to sell the computer at a salvage value of $200 at the end of 4 years.
IRS Asset Depreciation Guidelines
- Think of it as your asset’s future garage sale price after it’s done its duty for you.
- The double-declining balance method is a depreciation technique used to calculate the reduction in value of an asset over its useful life.
- As the salvage value is extremely minimal, the organizations may depreciate their assets to $0.
- Companies consider the matching principle when they guess how much an item will lose value and what it might still be worth (salvage value).
Salvage value might only focus on its worth when it’s done, without considering selling costs. Both declining balance and DDB methods need the company to set an initial salvage value. The straight-line method is a way to calculate depreciation by evenly spreading the asset’s cost over its useful life.
How is Salvage Value Calculated?
So, in such a case, the insurance company finally decides to pay for the salvage value of the vehicle rather than fixing it. The salvage calculator reduces the loss and assists in making a decision before all the useful life of the assist has been passed. Hence, a car with even a couple of miles driven on it tends to lose a significant percentage of its initial value the moment it becomes a “used” car. Under straight-line depreciation, the asset’s value is reduced in equal increments per year until reaching a residual value of zero by the end of its useful life. The impact of the salvage (residual) value assumption on the annual depreciation of the asset is as follows. The salvage value is considered the resale price of an asset at the end of its useful life.
How Salvage Value Is Used in Depreciation Calculations
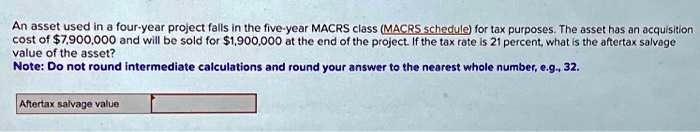
Salvage value is also known as scrap value or residual value and is used when determining the annual depreciation expense of an asset. The four depreciation methods available are straight-line, units of production, declining balance, and sum-of-the-years’ digits. The choice of method depends on the nature of the asset and its expected pattern of use and obsolescence. The after-tax salvage value is the net value of an asset after it has been sold and all related taxes have been deducted.
In some cases, salvage value may just be a value the company believes it can obtain by selling a depreciated, inoperable asset for parts. When calculating depreciation, an asset’s salvage value is subtracted from its initial cost to determine total depreciation over the asset’s useful life. From there, accountants have several options to calculate each year’s depreciation. An asset’s salvage value subtracted from its basis (initial) cost determines the amount to be depreciated. Most businesses utilize the IRS’s Accelerated Cost Recovery System (ACRS) or Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) methods for this process. The disposal value, also known as gross proceeds, is the amount received when selling or disposing an asset.
Salvage Value – A Complete Guide for Businesses
The first step is to determine this value by determining market prices for similar assets, referencing professional appraisals, or negotiating with potential buyers. Understanding after tax salvage value is a crucial component in determining the overall profitability of an investment or asset. It helps businesses and individuals estimate the net cash flow they will receive when disposing of an asset after taking into account the applicable tax consequences. In this article, we’ll walk you through the process of calculating the after tax salvage value. The salvage price of the asset and scrap value calculation are based on the original price and depreciation rate.
In the case of capital losses, they can often offset other capital gains or be carried forward to offset future gains. The salvage value calculator evaluates the salvage value of an asset on the basis of the depreciation rate and the number of years. The salvage value is calculated to know the expected value or resale value of an asset over its useful life. Salvage value can be considered the price a company could get for something when it’s all used up.
Each company has its way of guessing how much something will be worth in the end. Some companies might say an item is worth nothing (zero dollars) after it’s all worn out because they don’t think they can get much. But generally, salvage value is important because it’s the value a company puts on the books for that thing after it’s fully depreciated. Salvage value is the amount a company can expect to receive for an asset at the end of the asset’s useful life. A company uses salvage value to estimate and calculate depreciation as salvage value is deducted from the asset’s original cost.
Companies take into consideration the matching principle when making assumptions for asset depreciation and salvage value. The matching principle is an accrual accounting concept that requires a company to recognize expense in the same period as the related revenues are earned. If a company expects that an asset will contribute to revenue for a long period of time, it will have a long, useful life.
Each year, the depreciation expense is $10,000 and four years have passed, so the accumulated depreciation to date is $40,000. Scrap value might be when a company breaks something down into its satisfying tax requirements for verification » financial aid basic parts, like taking apart an old company car to sell the metal. To estimate salvage value, a company can use the percentage of the original cost method or get an independent appraisal.